Gray Gull Leucophaeus modestus Scientific name definitions
- LC Least Concern
- Names (31)
- Monotypic
Fernando Medrano, Ignacio Escobar Gutiérrez, and Rodrigo Silva
Version: 2.0 — Published December 23, 2022
Revision Notes
Revision Notes
Sign in to see your badges
Species names in all available languages
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Bulgarian | Сива чайка |
| Catalan | gavina grisa |
| Czech | racek tmavý |
| Danish | Atacamamåge |
| Dutch | Grijze Meeuw |
| English | Gray Gull |
| English (United States) | Gray Gull |
| Finnish | aavikkolokki |
| French | Goéland gris |
| French (France) | Goéland gris |
| German | Graumöwe |
| Greek | Λευκόστικτος Γλάρος |
| Icelandic | Sefmáfur |
| Japanese | ハイイロカモメ |
| Norwegian | ørkenmåke |
| Polish | mewa szara |
| Russian | Серая чайка |
| Serbian | Sivi mali galeb |
| Slovak | čajka púšťová |
| Spanish | Gaviota Garuma |
| Spanish (Argentina) | Gaviota Garuma |
| Spanish (Chile) | Gaviota garuma |
| Spanish (Costa Rica) | Gaviota Torero |
| Spanish (Ecuador) | Gaviota Gris |
| Spanish (Mexico) | Gaviota Gris |
| Spanish (Panama) | Gaviota Gris |
| Spanish (Peru) | Gaviota Gris |
| Spanish (Spain) | Gaviota garuma |
| Swedish | ökenmås |
| Turkish | Kül Rengi Martı |
| Ukrainian | Мартин сірий |
Revision Notes
Rodrigo Silva, Ignacio Escobar, and Fernando Medrano revised the account as part of a partnership with Red de Observadores de Aves y Vida Silvestre de Chile (ROC). Peter Pyle contributed to the Plumages, Molts, and Structure page. JoAnn Hackos, Robin K. Murie, Daphne R. Walmer, and Miriam Kowarski copy edited the account, August Davidson-Onsgard curated the media, and Huy Chi Truong generated the range map.
Leucophaeus modestus (Tschudi, 1843)
PROTONYM:
Larus modestus
Tschudi, 1843. Archiv für Naturgeschichte 9, p.389.
TYPE LOCALITY:
Shores of the Pacific Ocean = Lurin, south of Lima, Peru.
SOURCE:
Avibase, 2023
Definitions
- LEUCOPHAEUS
- leucophaeus
- modesta / modestum / modestus
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
UPPERCASE: current genus
Uppercase first letter: generic synonym
● and ● See: generic homonyms
lowercase: species and subspecies
●: early names, variants, misspellings
‡: extinct
†: type species
Gr.: ancient Greek
L.: Latin
<: derived from
syn: synonym of
/: separates historical and modern geographic names
ex: based on
TL: type locality
OD: original diagnosis (genus) or original description (species)
- Year-round
- Migration
- Breeding
- Non-Breeding
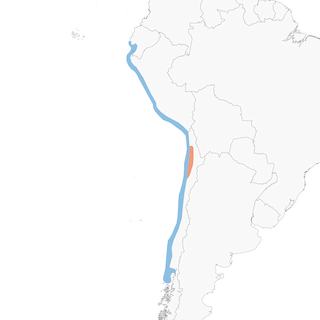
Distribution of the Gray Gull