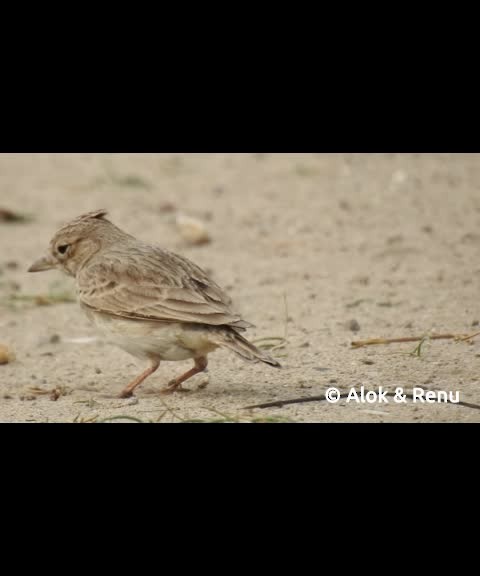
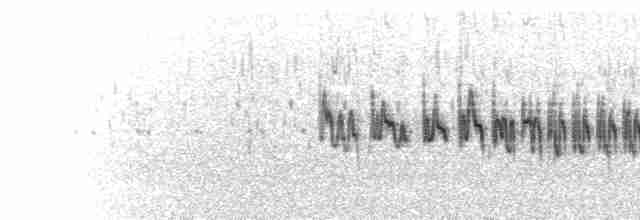
Sand Lark Alaudala raytal Scientific name definitions
- LC Least Concern
- Names (22)
- Subspecies (2)
Prasad Ganpule and Per Alström
Version: 2.1 — Published October 24, 2023
Revision Notes
Revision Notes
Sign in to see your badges
Species names in all available languages
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Catalan | terrerola de l'Índia |
| Czech | skřivánek indický |
| Danish | Indisk Dværglærke |
| Dutch | Indische Zandleeuwerik |
| English | Sand Lark |
| English (United States) | Sand Lark |
| French | Alouette raytal |
| French (France) | Alouette raytal |
| German | Uferlerche |
| Icelandic | Hærulævirki |
| Japanese | インドコヒバリ |
| Norwegian | sanddverglerke |
| Persian | چکاوک شنی |
| Polish | skowrończyk malutki |
| Russian | Песчаный жаворонок |
| Serbian | Peščarska mala ševa |
| Slovak | škovránok retal |
| Spanish | Terrera Raytal |
| Spanish (Spain) | Terrera raytal |
| Swedish | sandlärka |
| Turkish | Hint Çorak Toygarı |
| Ukrainian | Жайворонок крихітний |
Revision Notes
Per Alström standardized the account with Clements taxonomy.
Alaudala raytal (Blyth, 1845)
PROTONYM:
Alauda raytal
Blyth, 1845. Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal 13(1844), p.962.
TYPE LOCALITY:
Lucknow.
SOURCE:
Avibase, 2023
Definitions
- ALAUDALA
- raytal
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
UPPERCASE: current genus
Uppercase first letter: generic synonym
● and ● See: generic homonyms
lowercase: species and subspecies
●: early names, variants, misspellings
‡: extinct
†: type species
Gr.: ancient Greek
L.: Latin
<: derived from
syn: synonym of
/: separates historical and modern geographic names
ex: based on
TL: type locality
OD: original diagnosis (genus) or original description (species)
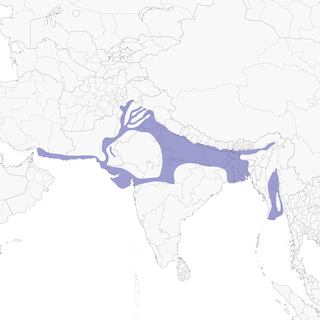
- Year-round
- Migration
- Breeding
- Non-Breeding
Distribution of the Sand Lark